GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) is a digital mobile network that is widely used in America and other parts of the world, many mobile phone customers use the GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) digital mobile network. The most popular of the three digital wireless telephony technologies—TDMA, GSM, and CDMA—GSM employs a version of time division multiple access (TDMA) (CDMA). GSM converts data to an electronic form, compresses it, and delivers it along with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot, down a channel. Either the 900 MHz or 1,800 MHz frequency bands.
The development of wireless mobile telecommunications has included several technologies, such as High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE), and Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service, in addition to GSM (UMTS).
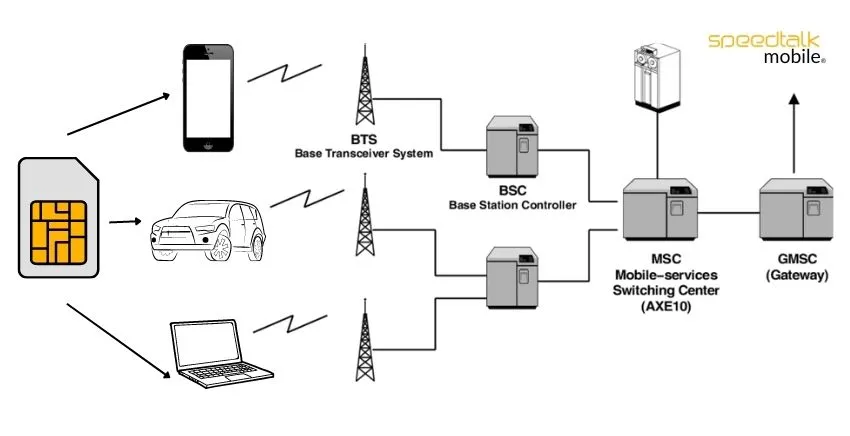
The GSM Network System works in (4) four separate parts that work together to function as a whole. The mobile device itself, the Base Station Subsystem (BSS). The Network Switching Subsystem (NSS) and the Operation and Support Subsystem (OSS).
Hardware is used to connect the mobile device to the network. The network receives identification data about the mobile user from the subscriber identity module (SIM) card.
Between the cellphone and the NSS, traffic is managed by the BSS. The base transceiver station (BTS) and the base station controller are its two primary parts (BSC). The BSC is the brains behind the BTS, which houses the hardware that interacts with mobile phones, primarily the radio transmitters, receivers, and antennas. The base transceiver stations are managed and in communication with by the BSC.
To facilitate the delivery of cellular services, the NSS component of the GSM network architecture, also known as the core network, tracks the position of callers. The NSS is owned by mobile operators. Mobile Switching Center (MSC), a component of the NSS, and Home Location Register (HLR). These parts carry out a variety of tasks, including as short message service (SMS) and call routing, as well as SIM card-based caller account authentication and storage.
Users frequently have access to their phones while traveling abroad because many GSM network operators have roaming agreements with foreign operators. Switching from SIM cards with home network access setups to ones with metered local access can drastically lower roaming expenses without affecting service.
GSM predecessors created with analog technology include Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) in the U.S. and Total Access Communication System (TACS) in the U.K. However, as more people adopted them, these telecommunications networks were unable to grow. These systems’ flaws highlighted the need for a more effective cellular technology that could be applied globally.
To accomplish this, a committee to create a European standard for digital telecommunications was established in 1983 by the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT). The CEPT established a number of requirements for the new system, including support for international roaming, excellent speech quality, support for handheld devices, affordable service costs, support for new services, and ISDN capability.
13 European nations signed a deal in 1987 to implement a telecommunications standard. Then, the European Union (EU) implemented legislation mandating GSM as the preferred standard throughout Europe. The GSM project was handed off from CEPT to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute in 1989. (ETSI).
In Finland, GSM-based mobile services were initially introduced in 1991. The GSM standard frequency band was increased from 900 MHz to 1,800 MHz in the same year. GSM accounted for 80% of the worldwide mobile market in 2010. However, a few of telecoms companies, like Telstra in Australia, have shut down their GSM networks. Singapore terminated its 2G GSM network in 2017.
Despite the fact that GSM was created as a secure wireless system, assaults are still possible. A pre shared key that takes the form of a password or passphrase is one of the authentication methods used by GSM. Another is challenge-response authentication, which asks a user for a correct response to a question.
Several cryptographic security algorithms, such as stream ciphers that encrypt numbers in plaintext, are used by GMS. Three stream ciphers known as A5/1, A5/2, and A5/3 guarantee the confidentiality of user communications. However, since the A5/1 and A5/2 algorithms have both been cracked and made public, plaintext assaults are possible.
GSM transmits data via GPRS, a packet-based communication service, for example when browsing the internet. But in 2011, GEA1 and GEA2, the GPRS ciphers, were also cracked and made public. To sniff GPRS packets, researchers released open source software.
The technology behind each of GSM, CDMA, and LTE (long-term evolution) cellular-wireless communications, as well as the business goals each is intended to achieve, are their primary differences. The oldest of the three is GSM. The processor/chip technologies in hand at the time were employed by GSM, which was created and adopted as a standard in Europe, to encrypt and decrypt data.
With the exception of the United States and a few South American countries, mobile operators briefly launched 2G GSM in many nations throughout the world. These exceptions were mostly caused by compatibility issues with analog AMPS systems already in use. They assessed the economies of scale offered by GSM for their networks in order to achieve the required temporary compatibility. Carriers used D-AMPS (Digital-Advanced Mobile Phone Service), a digital variant of AMPS built on Interim Standard (IS)-136 for TDMA networking, which was itself an evolution of the original 2GL D-AMPS standard, IS-54, from the Electronics Industries Association /Telecommunication Industry Association. However, it ultimately became apparent that TDMA protocols were not spectrum-efficient enough to sustain rapidly expanding cellular services. The development of CDMA protocols resulted from this.
In 1993, ITU IS-95, sometimes referred to as cdma One, was adopted as the CDMA digital cellular standard and quickly gained acceptance in nations still utilizing Analog AMPS systems. However, coding and decoding CDMA required substantially more computational power than coding and decoding TDMA, hence IS-95 required strong processors. Therefore, CDMA phones cost more than GSM versions.
From there, cellular technology developed. For data, cdmaOne gave rise to ANSI-2000 1xRTT, whereas GSM brought about GPRS, which paved the way for EDGE. That ultimately resulted in EV-DO. Wide-Band CDMA (W-CDMA) protocols were approved by 3GPP due to their improved efficiency for usage in 3G UMTS.
The data transfer speeds of 4G LTE, a GSM technology, are significantly faster than those of 3G. However, there is no standard phone call option available. LTE employs specialized voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) for what is known as VoLTE to make ordinary phone calls.
Through Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), the encoding technology used by LTE, CDMA and GSM eventually converged. Additionally, WiMAX and Wi-Fi networks use OFDMA as its encoding protocol.
New encoding protocols are anticipated to accompany 5G as it spreads in popularity. It’s still too early to say whether 5G will bring about a technical revolution in the telecommunications industry or a gradual evolution. In either case, the majority of those who follow the telecommunications sector concur that the impacts will be significant and of a large-scale.
New encoding protocols are anticipated to accompany 5G as it spreads in popularity. It’s still too early to say whether 5G will bring about a technical revolution in the telecommunications industry or a gradual evolution. In either case, the majority of those who follow the telecommunications sector concur that the impacts will be significant and of a large-scale.
GSM, and consequently its offspring 5G New Radio (NR), UMTS, and LTE, are more widely used than CDMA. Almost every nation in the world has GSM-based technology in use.
Contrarily, CDMA is now used in fewer than 10 nations. Additionally, in the following five years, carriers will shut down practically all of those CDMA networks.
What are some limitations of GSM?
The favored technology for today’s telecommunication networks is GSM, however it has drawbacks as well. The following are some GSM drawbacks:
Electronic interference. pulse-transmission method used by GSM is known to create interference with electrical devices like hearing aids. Mobile phones must be turned off in some locations, including airports, gas stations, and hospitals, due to electromagnetic interference. drawbacks:
Bandwidth lag. Multiple users share the same bandwidth when using GSM technologies, which can occasionally cause significant latency as additional users join the network.
Limited rate of data transfer. GSM has a somewhat slow data transfer rate. A user needs migrate to a gadget with more modern GSM forms in order to achieve better data rates.
Repeaters. Carriers must deploy repeaters in order to expand coverage with SIM technology.
The following are some GSM networks in the U.S.:
- AT&T
- T-Mobile USA Inc.
- Telecom North America Mobile Inc.
- SpeedTalk Mobile
- Union Wireless
- Viaero Wireless
- Cellular One
- Cordova Wireless
- Corr Wireless
- NEP Wireless
- Pine Cellular
- Plateau Wireless
- West Central Wireless
- XIT Communications
- Westlink
- DTC Wireless
- Epic PCS
- Earthtones
- Fuzion Mobile
- i-Wireless
- Indigo Wireless
- Immix